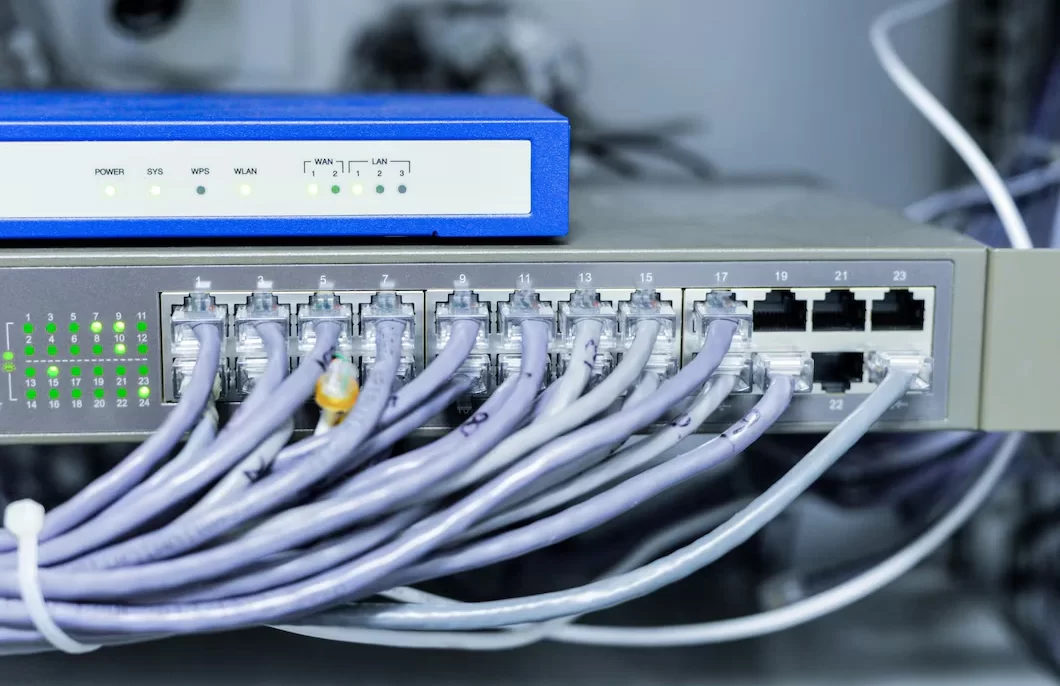

A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects numerous smaller Local Area Networks (LANs). WANs can provide communication, information sharing, and other activities between systems or devices from all over the world via a WAN provider.
What is WAN (Wide Area Network)?
The acronym WAN stands for Wide Area Network. It is a large-area computer network made up of two or more LANs or MANs. These networks are built using leased telecommunication circuits, where the two connected sides have routers that connect their LANs together in a network to allow communication.
Also Read:- MAN Network Explained
Pros of WAN
- It covers a broad geographical area, increasing an organisation’s ability to distribute data swiftly and affordably.
- Because of the WAN’s remote access to data, data can be stored centrally.
- The travel costs required to cover the geographical region of work might be reduced.
- WAN connects users and organizations globally, facilitating data sharing and business transactions.
Cons of WAN
- Traffic congestion in the Wide Area Network is extremely high.
- Due to the numerous connection points, there is a high level of noise and inaccuracy.
- Because of the long distances and the vast number of connected systems within the network, data transfer rates are slower than over a LAN.
Also Read:- What Is the Difference Between LAN, MAN, and WAN? (2025)
What is a Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN)?
A software-defined WAN, or SD-WAN, is a more adaptable WAN design that can leverage a variety of hardware platforms and connectivity options. The controlling software is compatible with any networking hardware.
SD-WANs are a type of software-defined networking (SDN), a set of technologies that enable network management through software. They are also an important component of secure access service edge (SASE) solutions, which bundle networking and network security tasks into a single cloud-based service.
Also Read:- What Is LAN?
What is WAN-as-a-Service?
WAN-as-a-service is a cloud-based WAN framework. WAN-as-a-service offerings are intended to replace older WAN configurations that are hardware-dependent, require communication protocols such as multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), and are difficult to scale up. Because WAN-as-a-service is delivered via the cloud, users simply require Internet access and may design their WAN using software rather than hardware appliances.
Key Features of WAN:
- Increased Capacity: WAN can accommodate a large number of LANs (Local Area Network) or other WANs so that a large number of users and devices throughout the world can be handled.
- Use of Public Carriers: WAN employs public facilities such as telephone lines, cables, and satellites for connecting and transmitting data, which are readily accessible and found nearly everywhere.
- Resource Sharing: WAN enables individuals to share data, files, and even computer resources over large distances. This facilitates the transmission of information and access to resources from anywhere.
- Wide Span: WAN spans a very large area such as state, national, or even global so that remote access can be gained by clients with ease.
- Dependable Communication: WAN is structured to maintain connections operational and active over distances, thus allowing businesses and users to remain connected without interruptions.
- Cost-Effective: As WAN utilizes public networks and infrastructure (such as phone lines or satellites), it will prove a more affordable method of connecting individuals over distances when compared to private networks.
- Scalability: WAN can scale as required with more users and devices being able to connect without any significant problems. This makes it ideal for expanding businesses or organizations.
Conclusion
WAN (Wide Area Network) is important for connecting people and businesses over long distances. It covers large areas, connects many devices, and makes it easy to share resources and information. With its use of public services, reliability, low cost, and ability to grow as needed, WAN is a key tool for networking today. Whether for personal or business use, WAN helps keep things running smoothly, no matter how far apart people are.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is WAN Network?
A WAN network is an arrangement of networked devices or local networks (LANs) distributed over a large area for facilitating communication and data exchange across far-off points. It is widely utilized in connecting branch offices or remote workers.
- How is WAN different from LAN?
A WAN spans a vast geographical area, e.g., a nation or the globe, whereas a LAN is confined to a small geographical area, e.g., a home or office. WAN interconnects several LANs and enables communication over a long distance.
- What are the benefits of employing WAN?
WAN offers the capability to link several devices or networks across long distances, enabling companies and individuals to exchange data, access resources remotely, and communicate efficiently regardless of their location.
- Explain WAN and how it operates.
WAN operates by employing technologies such as telephone lines, satellites, and fiber-optic cables to link several devices or networks distributed across vast distances. It facilitates the transfer of data from one location to another, providing communication and access to common resources on a worldwide scale.
- What are the technologies employed in WAN?
WAN employs technologies such as telephone lines, satellites, fiber optic cables, and other public communication networks to link users and transfer data over long distances.





0 Comments