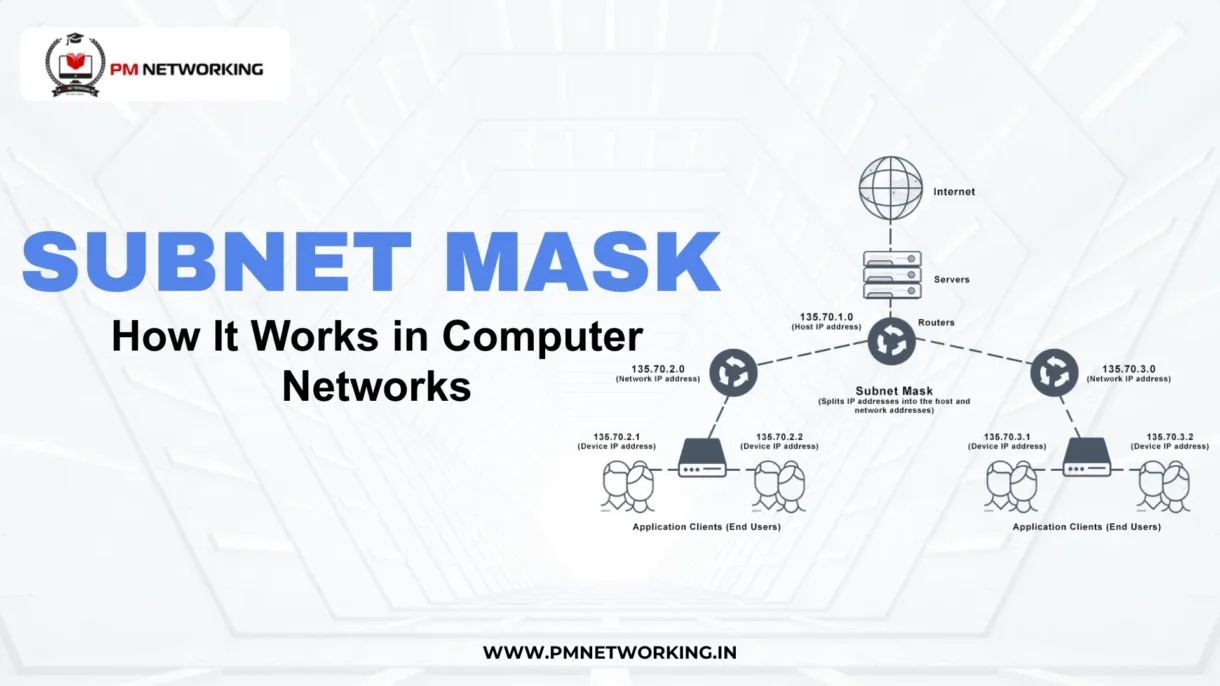
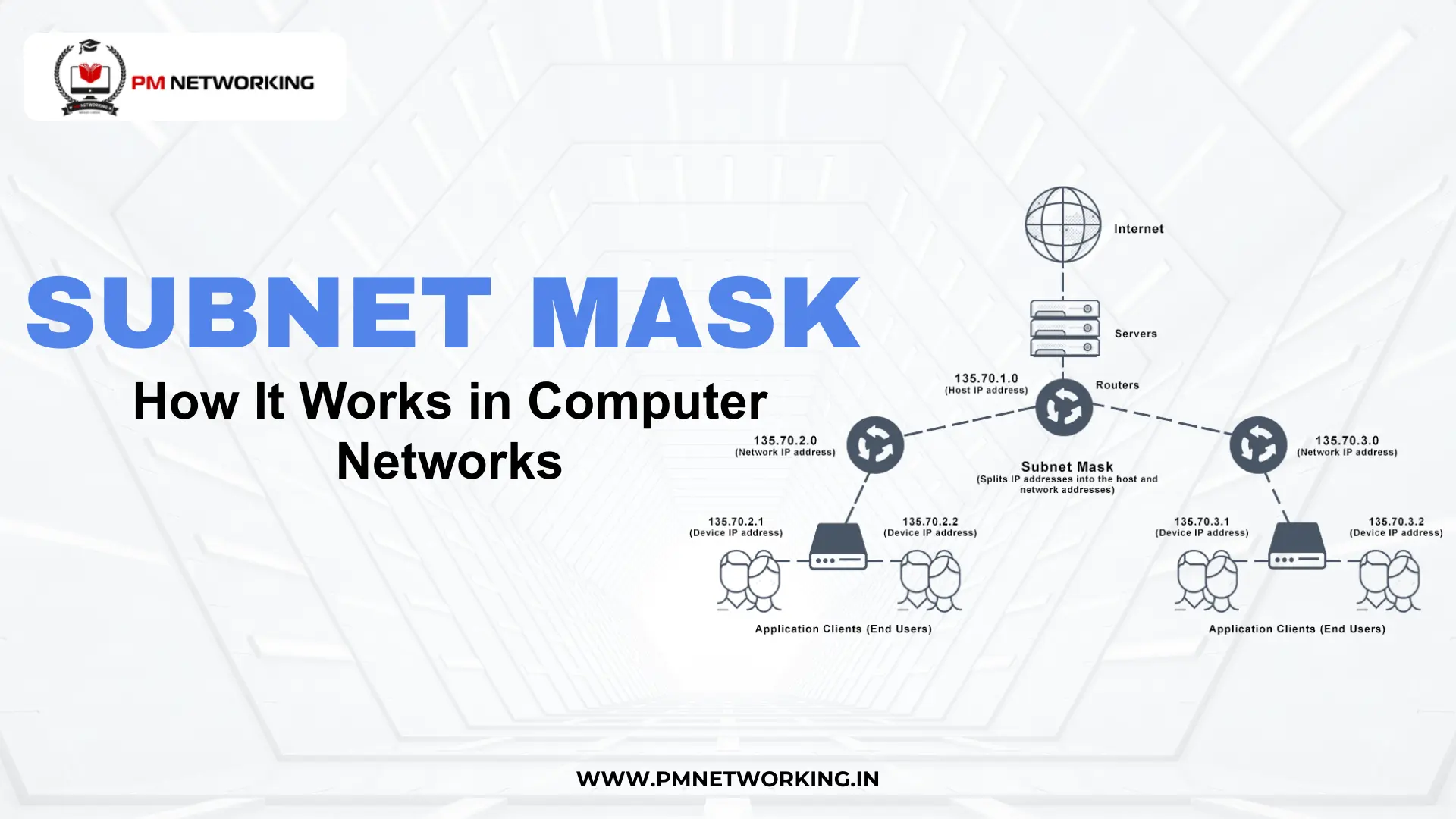
In this blog, Subnet Mask Explained: How It Works in Computer Networks, you will learn how a subnet mask separates network and host portions, how it controls traffic flow, and why it plays a critical role in performance, routing, and security. Whether you are a beginner in networking or preparing for certifications, mastering how subnet masks work will give you a strong foundation in network design and troubleshooting.
What Is a Subnet Mask?
A subnet mask is a number that helps divide a network into smaller parts called subnets. In simple words, it tells a computer which part of an IP address belongs to the network and which part belongs to a device. That is why understanding what is subnet mask is important for anyone learning networking.
A subnet mask works together with an IP address. The IP address identifies a device, but the subnet mask explains how that address is grouped inside a network. Since networks can be large, they are divided into smaller sections, and the subnet mask makes this possible.
In subnet mask in computer networks, the mask acts like a filter. It separates the network portion from the host portion of the IP address. Thus, devices can communicate properly because they know whether another device is in the same network or not.
Why Subnet Mask Matters in Networking
The importance of subnet mask becomes clear when networks start growing. In small networks, managing devices is easy, but large networks can become confusing. A subnet mask helps divide a big network into smaller parts, thus making it more organized and easier to manage.
Another reason why subnet mask is used is to improve performance. When a network is divided into subnets, traffic stays inside its own section. Because of this, devices do not have to deal with unnecessary data, and the network runs faster and more smoothly.
There are many subnet mask uses, especially in security and routing. Subnets can limit access between groups of devices, which helps protect sensitive data. Also, routers use subnet masks to decide where to send data, hence ensuring the information reaches the correct network.
How Subnet Mask Works
To understand how subnet mask works, remember that an IP and subnet mask always work together. The IP address shows the device, but the subnet mask shows which part is the network and which part is the device.
Step 1: Binary AND operation
Computers use 0s and 1s. The subnet mask compares its numbers with the IP address using a simple rule called AND. If both numbers are 1, the result is 1. If not, the result is 0. This helps find the network part.
Step 2: Network part and host part
In a subnet mask, 1s mean network. 0s mean host (device). Because of this, the computer can clearly separate the network section from the device section.
Step 3: Subnet bits separate networks
More 1s in the mask mean more network bits. This creates more subnets but fewer devices in each. Hence, network size can be controlled easily.
Subnet mask example:
Take 192.168.1.10 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Here, 192.168.1 is the network part, and 10 is the device part. So all devices starting with 192.168.1 are in the same network. This simple subnet mask example shows how it works.
Understanding Subnet Mask Values
There are common subnet mask values that are used in most networks. These numbers may look confusing at first, but they follow a simple pattern.
255.0.0.0
This mask means the first part is the network, and the rest is for devices. It is written as /8 in CIDR form. This allows a very large number of devices in one network.
255.255.0.0
Here, the first two parts are for the network. It is written as /16. This is used for medium-sized networks.
255.255.255.0
This is one of the most common masks. It means the first three parts are the network. It is written as /24. Many small networks use this mask.
This short form like /8, /16, /24 is called CIDR notation. Understanding cidr and subnet mask together helps you read networks easily. The number after the slash shows how many bits are used for the network.
Subnet mask conversion simply means changing the mask from number form (255.255.255.0) to CIDR form (/24) or the other way around. Both mean the same thing, but CIDR is shorter and easier to write.
Subnet Mask in Different Network Types
A network subnet mask is used in many types of networks, but the purpose is the same. It divides networks into smaller parts so devices can communicate properly.
Subnet mask in LAN (Local Area Network) is very common. Homes, schools, and offices usually use 255.255.255.0. Since LANs are smaller, this mask works well.
In a WAN (Wide Area Network), subnet masks are used to connect networks over long distances. These networks may use different mask sizes depending on how many devices are connected.
In enterprise networks, subnet masks are very important. Large companies divide their network into many subnets for better performance and security. Hence, subnetting helps keep big networks organized and safe.
Practical Use Cases
There are many real-life subnet mask use cases in networking. It is not just theory, but something used every day.
One of the main examples of subnet mask is in company network division. A company may separate departments like HR, Sales, and IT into different subnets. This keeps traffic organized and improves security.
Subnet masks also help with IP allocation efficiency. Instead of wasting IP addresses, networks can be divided properly. Because of this, IP space is used wisely.
They also help in network performance tuning. When networks are divided into smaller subnets, traffic is reduced. Thus, the network becomes faster and more stable.
Subnet Mask vs Netmask vs CIDR
Many people get confused between netmask vs subnet mask, but they are almost the same.
- Subnet Mask – Used to divide a network into smaller subnets.
- Netmask – Another name for subnet mask. There is no big difference.
- CIDR Subnet Mask – A shorter way to write the subnet mask using “/” format like /24.
So when comparing cidr subnet mask with the normal format, remember they show the same thing. For example:
255.255.255.0 = /24
The only difference is how they are written.
Common Errors With Subnet Masks
There are some common subnet mask errors that can cause network problems.
One issue happens when the wrong mask is used. Devices may not reach each other, although they look like they are in the same network. This is a common problem in offices.
Another problem is mismatched subnet ranges. If two devices have different subnet masks, they may not communicate properly. Because of this, connection failures happen.
Good subnet mask troubleshooting includes checking the IP address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway. Even a small mistake can stop the network from working.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of subnet mask is essential for anyone working in networking. It helps divide networks, improve performance, and increase security.
This guide on subnet mask explained shows that although the concept may look technical, it is actually simple. Once you understand how it separates network and host parts, everything becomes clearer.
Hence, learning subnet masks is a basic but powerful step toward becoming a skilled network engineer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a subnet mask in simple words?
A subnet mask is a number that separates the network part as well as the device part of an IP address. It helps devices know if they are in the same network or if they are not.
2. Why is a subnet mask important?
The importance of subnet mask is that it organizes networks and improves performance. It also helps in routing as well as basic network security.
3. What is the difference between CIDR and subnet mask?
CIDR is just a shorter way to write a subnet mask like /24 instead of 255.255.255.0. Although both mean the same thing, CIDR is comparatively easier to read and write.
4. How do you calculate subnet mask from CIDR?
To calculate a subnet mask from CIDR, count the number after the slash. For example, /24 means 24 bits are used for the network, which equals 255.255.255.0.
5. What is the role of a subnet mask in routing?
Routers use subnet masks to determine the destination network of a packet. This ensures data is forwarded to the correct network path.




0 Comments