The routing protocols used within modern enterprise networks, such as the OSPF routing protocol, are used to facilitate the transfer of data from one place to another. Although there are many routing protocols available, not all of them are suitable for large and complex networks and this is where OSPF comes in. It is widely used in enterprise environments since it is fast, reliable, and designed to handle growth. Thus, understanding how OSPF works becomes essential for network engineers and IT professionals.
What Is OSPF Routing Protocol?
OSPF is a dynamic link-state routing protocol that is used to determine the best possible path for data to travel across a network. This allows for more efficient routing of data as it works by calculating routes based on cost, not just distance. Because OSPF routers constantly share updates about the network, OSPF can react quickly to changes, although the network may be large or complex.
In enterprise networks, OSPF is widely used since it supports scalability, fast convergence, and stable routing. It allows networks to be divided into areas, thus reducing unnecessary routing traffic and improving overall performance. This makes OSPF a strong choice for businesses that need reliable communication between departments and locations.
The full form of OSPF is Open Shortest Path First, and it operates using IP protocol number 89. Compared to RIP, which is slower and limited in size, and BGP, which is designed for internet-scale routing, OSPF is best suited for internal enterprise networks.
If you want to understand how OSPF is used in real enterprise networks with hands-on configuration, the CCNA 200-301 Course explains these concepts step by step.
OSPF Protocol Full Form and Protocol Number
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First, and it is used to find the best path for data inside a network. The name may sound technical, but the idea is simple because OSPF always chooses the shortest and most efficient route, thus improving network performance.
OSPF uses protocol number 89 for both IPv4 and IPv6. This number matters in networking because it tells devices how to recognize and handle OSPF traffic. Since OSPF runs directly over IP and not TCP or UDP, routing updates are exchanged faster and more efficiently.
Because OSPF integrates directly with IP routing, it can quickly share network information between routers. Although networks may change often, OSPF adapts smoothly, thereby ensuring stable and reliable communication across the enterprise network.
Key Features of OSPF
- Link-state routing protocol
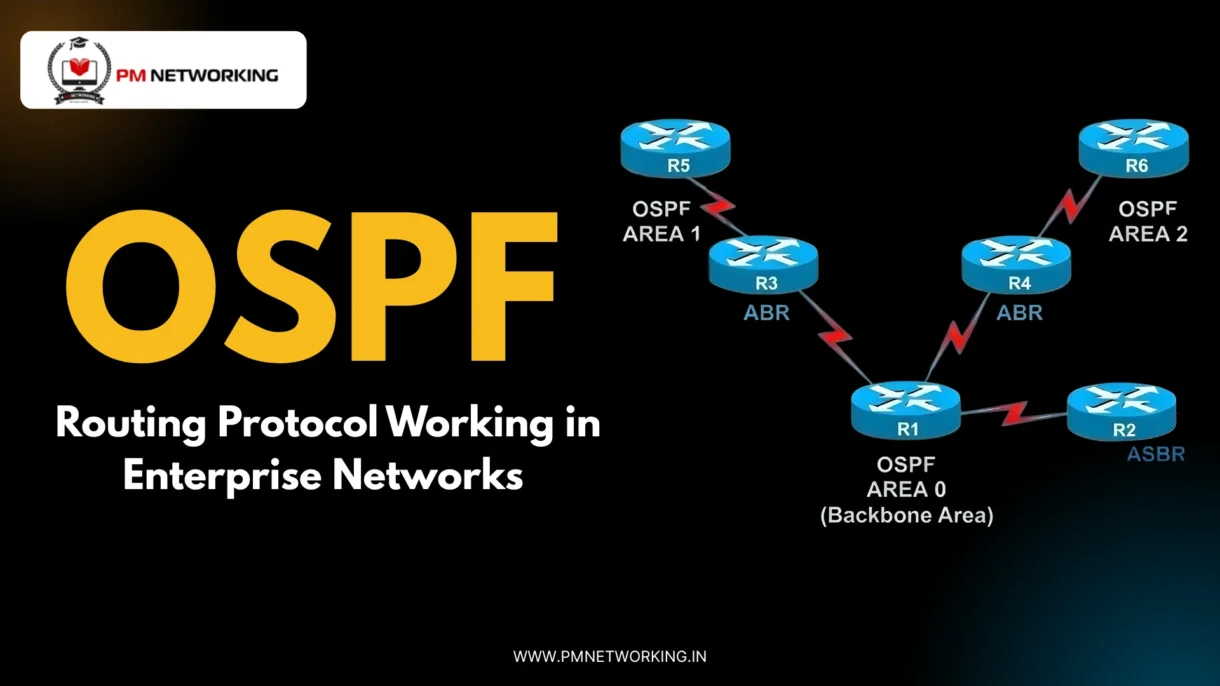
OSPF works as a link-state protocol, which means each router knows the full network map. Because of this, it can make smart routing decisions, thus sending data through the best possible path. - Hierarchical network design (Areas and Area 0)
OSPF uses areas to organize large networks, but all areas connect to Area 0, also called the backbone. This design reduces traffic and confusion, thereby making the network easier to manage. - Fast convergence and scalability
OSPF reacts quickly when a link goes down or comes back up. Since enterprise networks are large, this fast convergence helps keep data flowing smoothly even during changes. - Support for VLSM and CIDR
OSPF supports VLSM and CIDR, which allows better use of IP addresses. Because of this, networks avoid wasting address space and stay more efficient. - Authentication and security features
OSPF supports authentication so only trusted routers can share routing information. Although networks may face security risks, this feature helps keep routing updates safe and reliable.
How OSPF Works
OSPF shares network information using Link-State Advertisements (LSAs). These messages inform routers about link status, and because they are shared often, routers stay updated and can react quickly to changes.
All LSAs are stored in the Link-State Database (LSDB). Every router in the same area keeps the same database, thus they all see the same network layout.
OSPF uses Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to find the best path. It calculates the lowest-cost route, thereby sending data in the most efficient way.
Routers find each other using hello messages and form neighbors. In larger networks, a Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR) manage updates, thus reducing network traffic.
OSPF vs Other Routing Protocols (RIP, BGP)
OSPF, RIP, and BGP are all routing protocols, but they are used for very different purposes. RIP is simple but limited, OSPF is designed for internal enterprise networks, and BGP is mainly used to route traffic across the internet. Because of these differences, each protocol fits a specific network need.
OSPF has many advantages in comparison with RIP since it converges faster and supports large networks. Although RIP is easy to configure, it uses hop count and reacts slowly to changes. OSPF, on the other hand, uses cost-based routing, thus making it more efficient and reliable for growing enterprise environments.
In enterprise networks, OSPF is used for internal routing, while BGP is used when connecting to ISPs or other external networks. Although both are powerful, OSPF works best inside the organization, whereas BGP handles routing between different organizations, thereby keeping large-scale networks stable.
Advantages and Limitations of OSPF
OSPF has many advantages that make it popular in enterprise networks. It converges fast, so traffic keeps flowing even when links change. Because it is scalable and supports VLSM, IP addresses are used more efficiently. OSPF also uses a hierarchical design with areas, thus making large networks easier to manage.
However, OSPF also has some limitations. It is more complex to configure and understand, although simpler protocols like RIP are easier to set up. OSPF also uses more memory and CPU because it maintains a full network map, thereby increasing router resource usage. The configuration process can feel heavy in smaller networks.
OSPF is the preferred choice when networks are large, need fast recovery, and require flexible IP addressing. Although it may not be ideal for very small setups, OSPF works best in enterprise environments where performance and reliability matter most.
Conclusion
OSPF works by sharing network information, making a map of the network, and choosing the best path for data. Because of this, routers can send data quickly and reliably.
It is important in enterprise networks since it handles large networks well, reacts fast to changes, and keeps communication stable.
Learning OSPF is also useful for CCNA/CCNP and real-world networking because it helps you design, manage, and troubleshoot networks more confidently.
FAQs
What is OSPF protocol and why is it used?
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a routing protocol that is used to find the best path for data in a network. It is used because it is fast, reliable, and works well in large networks.
What is OSPF protocol number and full form?
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and uses protocol number 89 for both IPv4 and IPv6.
How OSPF routing protocol differs from RIP and BGP?
OSPF is faster and more scalable than RIP, and it works inside networks, while BGP is mainly for internet or external routing.
Can OSPF work in IPv6 networks?
Yes, OSPF can work with IPv6 using a version called OSPFv3, thus supporting modern networks.
What are the key OSPF areas in enterprise networks?
The main OSPF areas are Area 0 (Backbone) and other non-backbone areas, which help organize large networks and reduce traffic.





0 Comments