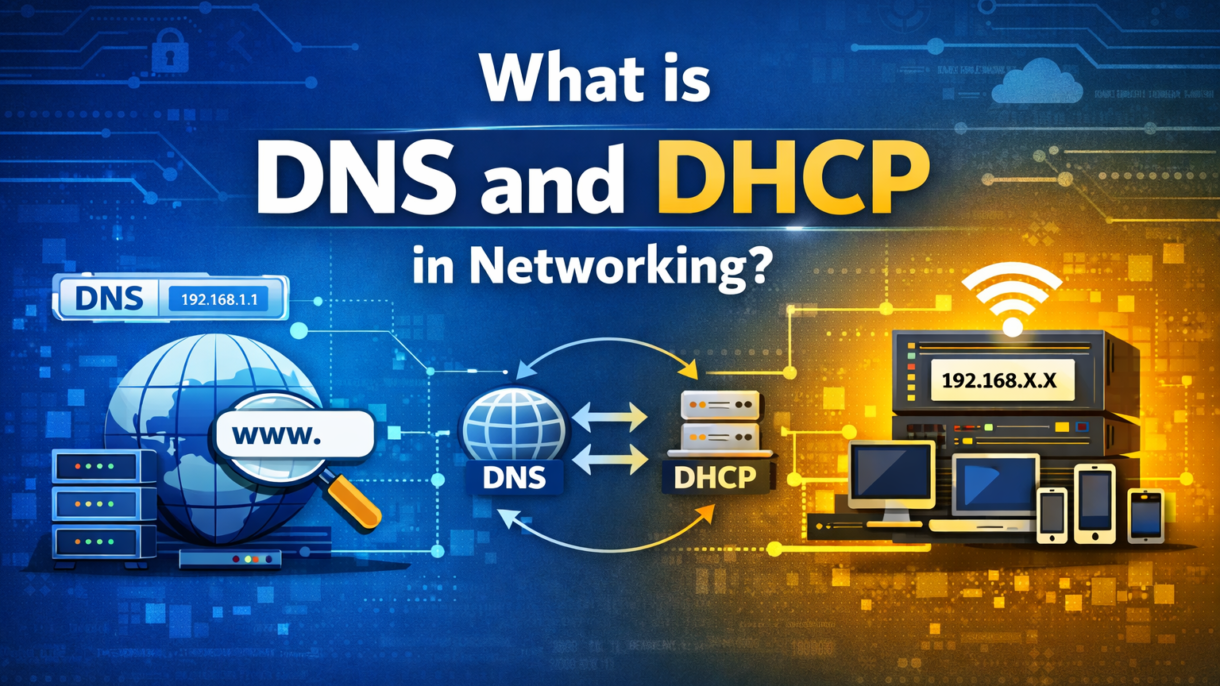
If you have ever wondered how your computer obtains its IP address automatically or how typing google.com instantly opens a website, then you have experienced both DHCP and DNS.DHCP and DNS are two essential network services that make life easier for both users and network administrators. DHCP assigns devices an IP address and DNS translates website names into IPs, thus keeping networks running smoothly and efficiently.
What is DHCP in Networking?
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network service that automatically gives devices an IP address so they can communicate on a network. Without it, you would have to assign IP addresses manually, which can be confusing and slow, especially in large networks.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) works in a simple 4-step process.
Discover → Offer → Request → Acknowledge
First, a device asks the network for an IP (Discover), then the DHCP server offers one (Offer). The device requests that IP (Request), and the server confirms it (Acknowledge). This process happens quickly, thus connecting devices to the network almost instantly.
Understanding DHCP also helps explain the dhcp and dns difference: DHCP handles IP addresses, while DNS translates names into IP addresses. Both work together to make networks easy to use.
A real-life example is your Wi-Fi network at home or office. When you connect your phone or laptop, DHCP automatically assigns it an IP so you can browse the internet without requiring any manual setup.
What is DNS in Networking?
DNS (Domain Name System) is a network service that works with DHCP to help devices find each other on the internet or a network. While DHCP gives a device an IP address, DNS translates easy-to-remember domain names, like google.com, into that IP address so data can reach the right place. If DNS records become outdated or incorrect, websites may fail to load properly, and in such cases, clearing the DNS cache is a common troubleshooting step to refresh DNS information.
When you type a website name in your browser, DNS quickly finds the corresponding IP address, thus allowing your device to connect to the site. This process is called IP address resolution and happens almost instantly.
There are different types of DNS servers: Primary and Secondary servers store the domain information, Recursive servers help find the IP for a domain, and Root servers guide queries to the right top-level domain. All these servers work together, thus making internet browsing fast and reliable.
A real-life example is when you open google.com in your browser. DNS translates that name into an IP address, allowing your device to connect to Google’s server without you ever seeing the numbers.
DHCP and DNS Difference
When you understand the dhcp and dns difference, you will see how they perform different functions. Both DHCP and DNS are essential for networks, but they perform completely different tasks. DHCP provides devices IP addresses automatically, while DNS helps translate website names into IP addresses so devices can connect.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | DHCP | DNS |
| Function | Assigns IP addresses | Resolves domain names |
| Protocol | UDP | UDP/TCP |
| Example | Connecting to Wi-Fi | Visiting a website |
How DHCP and DNS Work Together
When a device joins a network, it first gets an IP address from DHCP and then uses DNS to translate website names into IPs. Both are crucial because without DHCP, devices can’t connect, and without DNS, users can’t reach websites easily. If either service fails, the device may stay offline or websites may not load properly. When DNS fails to resolve domain names correctly, users may face website loading errors, which can often be fixed by refreshing DNS records in the browser. This is why checking DHCP and DNS settings is one of the most important troubleshooting steps in networking.
Common DHCP and DNS Issues
DHCP Issues:
One common DHCP issue is IP conflicts, which happen when two devices accidentally receive the same IP address. Another issue is lease expiration, where a device loses its IP address when the assigned lease runs out and/or expires.
These problems can usually be fixed by restarting the device or manually renewing the IP address from the network settings.
DNS Issues:
DNS can experience issues due to incorrect entries, where a wrong IP is stored for a domain, or server failure, when the DNS server goes down and websites fail to load.
However, most of these issues can often be resolved by:
- Clearing the DNS cache;
- Utilizing another DNS server, or
- Verifying the network settings
Understanding these common issues and how to fix them is essential for keeping networks running smoothly as well as efficiently.
Conclusion
DHCP and DNS are essential network services used to keep devices connected and websites accessible. DHCP assigns IP addresses to devices automatically and DNS translates domain names into IPs, thus making networks simple and efficient.
Understanding how DHCP and DNS work is important for anyone learning networking because it helps in setting up networks, managing devices, and troubleshooting problems quickly. A network without DHCP and DNS would be slow, confusing, and hard to manage.
To improve your networking skills, learn more networking fundamentals. This knowledge will help you troubleshoot issues efficiently and keep networks running smoothly as well.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between DHCP and DNS?
DHCP gives devices an IP address automatically, while DNS translates website names into IP addresses. Both work together to make networks run smoothly.
2. Can a network work without DHCP or DNS?
A network can work without them, but devices would need manual IPs, and websites would be hard to reach, making the network slow and confusing.
3. How does DHCP assign IP addresses automatically?
DHCP assigns IPs using a quick process: Discover → Offer → Request → Acknowledge, giving each device a unique IP without manual setup.
4. How does DNS resolve domain names to IP?
DNS looks up the IP address for a website name and sends it to your device, thus letting you access websites easily.
5. Why are DHCP and DNS important for network troubleshooting?
If devices can’t connect or websites won’t load, checking DHCP and DNS is usually the first step to fix the problem efficiently.




0 Comments