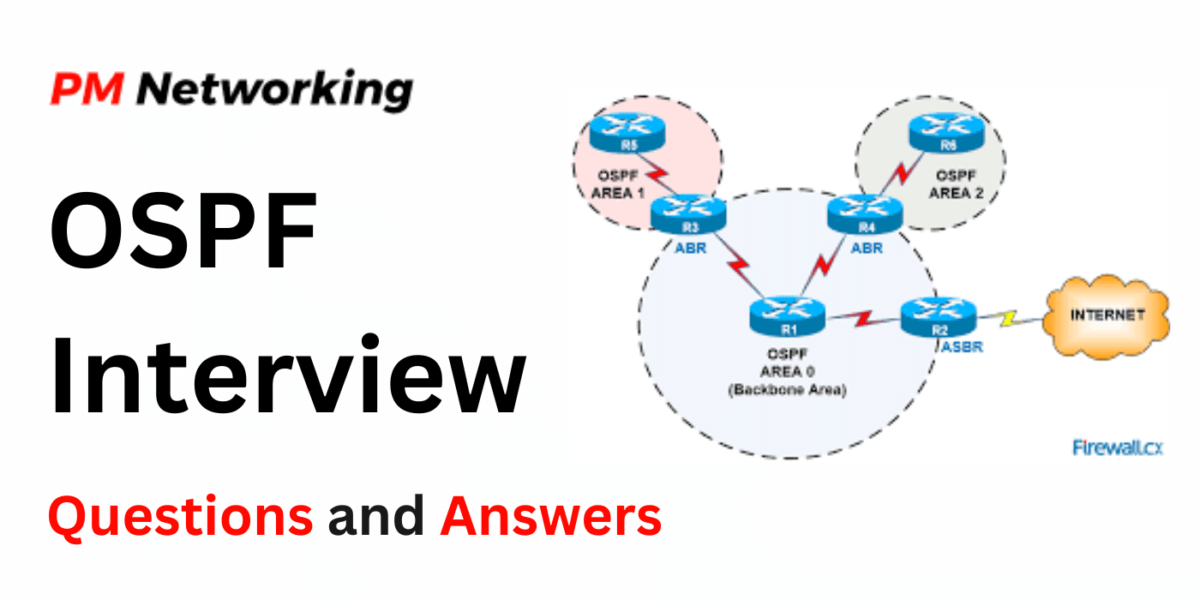
For both fresh and experienced candidates, there are top 20+ OSPF Interview Questions listed below. These questions will help you prepare better for the interview, answer confidently, and get OSPF Jobs quickly.
1. What is the OSPF routing protocol?
The term “OSPF” stands for “Open Shortest Path First“. It is an open average link-state routing protocol that uses the SPF algorithm developed by Dijkstra to determine the shortest and direct path. The resulting best path is used to populate the routing database.
2. How can we change the router ID in the OSPF domain?
After the OSPF method is initialized and OSPF neighbor ships are identified, the OSPF router ID should not be used inappropriately. For the modified RID to take effect, we must either reload the IOS or invoke the “#clear IP OSPF process authority” command.
3. What are the important features of OSPF?
Important features of OSPF are given below:
- It is a network layer protocol that works on protocol number 89.
- In the IP part, it provides TCP/IP model routing data.
- For normal communication, it uses multicast addresses 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6 to update the router.
- It is more effective at sending routing information because it deals with less traffic than Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
- The algorithm used is Shortest Path First (SPF).
4. What are the key features of OSPF?
The following are the major features of OSPF:
- Equal Cost Route Management: CEF Load Compatible
- OSPF’s Protocol Type: Link State
- Transport: IP (Port89) Submit to Network Walk website
- OSPF’s metric: cost (bandwidth)
- Standards: RFC2328 (OSPFv2), RFC2740 (OSPFv3/IPv6)
5. How does OSPF work?
The OSPF protocol is used by routers to broadcast routing data and any related updates to the table. OSPF sends only the part of the table that has been changed; This does not send the entire table. This configuration data is stored using a link state database. It will use this information to choose the fastest and best path to transfer the data packet to the destination.
6. Name the different types of OSPF
The following are the different types of OSPF:
- LSA Type 1: Router LSA
- LSA Type 2: Network LSA
- LSA Type 3: Summary LSA
- LSA Type 4: Summary ASBR LSA
- LSA Type 5: Autonomous System External LSA
- LSA Type 6: Multicast OSPF LSA
- LSA Type 7: Not Too Stubby Area LSA
- LSA Type 8: External Attribute LSA for BGP
- LSA Type 9: Link Scope Opaque (OSPFv2) / Intra Area Prefix LSA (OSPFv3)
- LSA Type 10: Area Scope Opaque LSA
- LSA Type 11: AS (Autonomous System) Scope Opaque LSA
7. What are the different functions and functionalities of OSPF?
The various functions and functionalities of OSPF are given below:
- OSPF determines the shortest path using the Dijkstra Shortest Path First algorithm.
- OSPF establishes neighbor associations with nearby routers in the same area.
- OSPF implements a hierarchical network design Using areas.
- OSPF supports VLSM and is a classless protocol.
- When one of its links changes, OSPF sends updates (LSAs) and will only send changes at that time. Additionally, the LSA is updated every 30 minutes.
- OSPF uses link-state advertisements rather than network distance-connected (LSA) to broadcast link state directly.
8. What benefits we will find after dividing the entire network into multiple areas?
Dividing the entire network into areas has the following advantages:
- This can limit network instability to particular areas of the network.
- Routing overhead is reduced.
- This could speed up convergence.
9. What is OSPF hello and dead interval?
OSPF uses two timers and Hello packets to determine whether a neighboring router is active.
- Hello interval specifies how often an OSPF router sends Hello packets. For point-to-point links, the default interval setting is 10 seconds. This period should be the same for shared networks.
- Dead interval specifies how long a router will wait before considering a neighboring router as dead. Depending on the type of network, the hello and dead interval values may differ.
10. What is DR and BDR in OSPF?
To exchange information between different routers in OSPF, a Backup Designated Router (BDR) and Designated Router (DR) are used. Depending on the network, one router is selected as DR and the other as BDR.
DR serves as the point of contact for network segments in each broadcast network. All routers move closer to the DR while handling all the LSAs in the network. The router uses the multicast address 224.0.0.6 to send DR information.
A BDR is chosen for the network to prevent problems in case the DR fails. When DR fails, it turns on and starts listening to the multicast address 224.0.0.6.
Check Out Our Popular Courses
11. What is the DR and BDR election process?
An OSPF router selects one router as DR and the other as BDR depending on the type of network. There is no BDR or DR election on a point-to-point network because the routers are directly connected. The router with the highest OSPF priority in the LAN is selected as the DR. By default, the priority is set to 1. If two routers have the same priority then the router with the highest router ID will be chosen. The next router is selected as the BDR because it has the highest router ID or second-highest priority.
12. What are the different network types of OSPF?
The different network types of OSPF are given below:
- Broadcast Network Type: In this form of network, data packets are transferred from one router to multiple routers.
- Point-to-Point Network Type: In this network type data packets are exchanged between exactly two routers.
- Non-broadcast network type: This network type allows access from a wide range of devices but does not allow broadcasting.
13. What is Router ID?
A router ID is used to uniquely identify each OSPF router. Each router is assigned an IPv4 address-based ID. A duplicate of this ID would prevent two routers from being neighbors, so it should not exist. This ID is also used by OSPF and BGP to identify the originating router from which a packet originated.
14. What is the role of the topology and routing table in OSPF?
Using the OSPF process, three different tables are created and maintained:
- Topology table: The routes of all known networks in the area are listed in this table.
- Neighbor Table: All neighbor routers are listed in this table.
- Routing Table: The best route is listed in this table for each known network.
15. What is the full form of LSA, LSU, and LSR in OSPF?
LSA is known as Link State Advertisement in OSPF. It is used to transmit basic topology information for routing to other nearby routers in the link state database. LSA data is added to the link state database by OSPF. Routers trade these LSAs until each router can access the same topology database.
- LSA = Link State Advertisement
- LSU = Link State Update
- LSR = Link State Request
In OSPF, LSAs are known as link-state advertisements. It is used to send basic topology information to other adjacent routers for routing purposes in the link state database. OSPF adds LSA data to the link state database. Routers trade these LSAs until each router can access the same topology database.
16. How can you turn neighboring ships into adjacent ones?
To convert neighboring ships into adjacent space we need to follow the given steps:
- To create a link, we must first make a state request. LSU packets will be communicated by this URL.
- Both routers will now trade Database Description packets to ensure database synchronization.
- Both routers can be measured as adjacent routers after the database synchronization is completed.
17. Why is OSPF called a loop-free protocol?
Because of the link-state database, OSPF is known as a loop-free protocol. With OSPF, the routing loops typical of distance vector protocols are avoided due to the comprehensive view of the network’s database. By using inter-area loop-free topology, OSPF prevents loops. For this reason, it is known as a loop-free protocol.
18. What are the different OSPF router types?
Below are the different OSPF router types:
- Internal Router: Internal routers are OSPF routers with similarly grouped interfaces.
- Backbone Routers: OSPF routers that serve as internal routers in Area 0 are known as backbone routers.
- Autonomous System Border Router: The type of OSPF routers that promote external routes in an OSPF domain are known as Autonomous System Border Routers.
- Area Border Router: The type of OSPF router known as an area border router has interfaces in multiple areas.
19. What do you understand by link-state retransmit interval?
Each new legacy LSA receives an acknowledgment from OSPF. LSAs are submitted repeatedly until accepted.
The link state retransmission interval determines the period between retransmissions. To set the retransmit interval, we can use the ip ospf retransmit-interval command.
Check Out Our Popular Courses
20. Is it possible to number one side and leave the other side unnumbered in OSPF?
No, in OSPF, it is not possible to number one side and leave the other side unnumbered. If you attempt to do this, the OSPF database will become inconsistent and routes will not be inserted into the steering table.
21. What do you understand by OSPF adjacency?
Through OSPF adjacency, link state advertisements (LSAs) can be sent to neighbors because of their potential connectivity.
22. What are the five OSPF packet types?
Below are the five types of OSPF packets:
- DBD
- HELLO
- LSU
- lSR
- ALSAC
23. What are the issues that DR and BDR solve in OSPF?
The following are the issues that DR and BDR solve in OSPF:
- Extreme LSA flooding
- A high number of proximity
24. What do you understand by OSPF Router ID??
The ID used to identify the router is called the OSPF Router ID, and it is a 32-bit number. The OSPF protocol can be used with a GRE tunnel.
Conclusion
To pass the OSPF exam in one go, you can opt for the PGP Full Stack Web Developer – Mean Stack Program. Through this full-stack MEAN developer program, you will study cutting-edge skills such as GIT, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript as well as MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js (“MEAN”) for interactive development and deployment of applications and Services.
Check Out Our Popular Courses




0 Comments