
- It is an IGP Protocol.
- It is a Link State Routing protocol (LSRP).
- Link means How many links are there between Routers.
- State means How many routers are connected with each link.
- In OSPF, routers do not advertise routes In fact routers advertise the complete database in the form of link state Advertisements (LSA). LSAs are advertised among the complete topology.
- Routers calculate their best path by checking their own database. It means routers are not dependent on their neighbor.
- OSPF Metric = Cost = Reference Bandwidth /Bandwidth of link.
- By default, the Reference Bandwidth is 100 Mbps. In some cases, we need to change the reference bandwidth.
- By default, the Maximum path that an OSPF Router can install in their routing table is 4 but we can change it up to 16/32.
- OSPF Routers sends a hello message to their neighbor after every 10 sec and the neighboring routers hold the information for 40 sec. You can say, OSPF Hello time is 10 sec and Hold time is 40 sec.
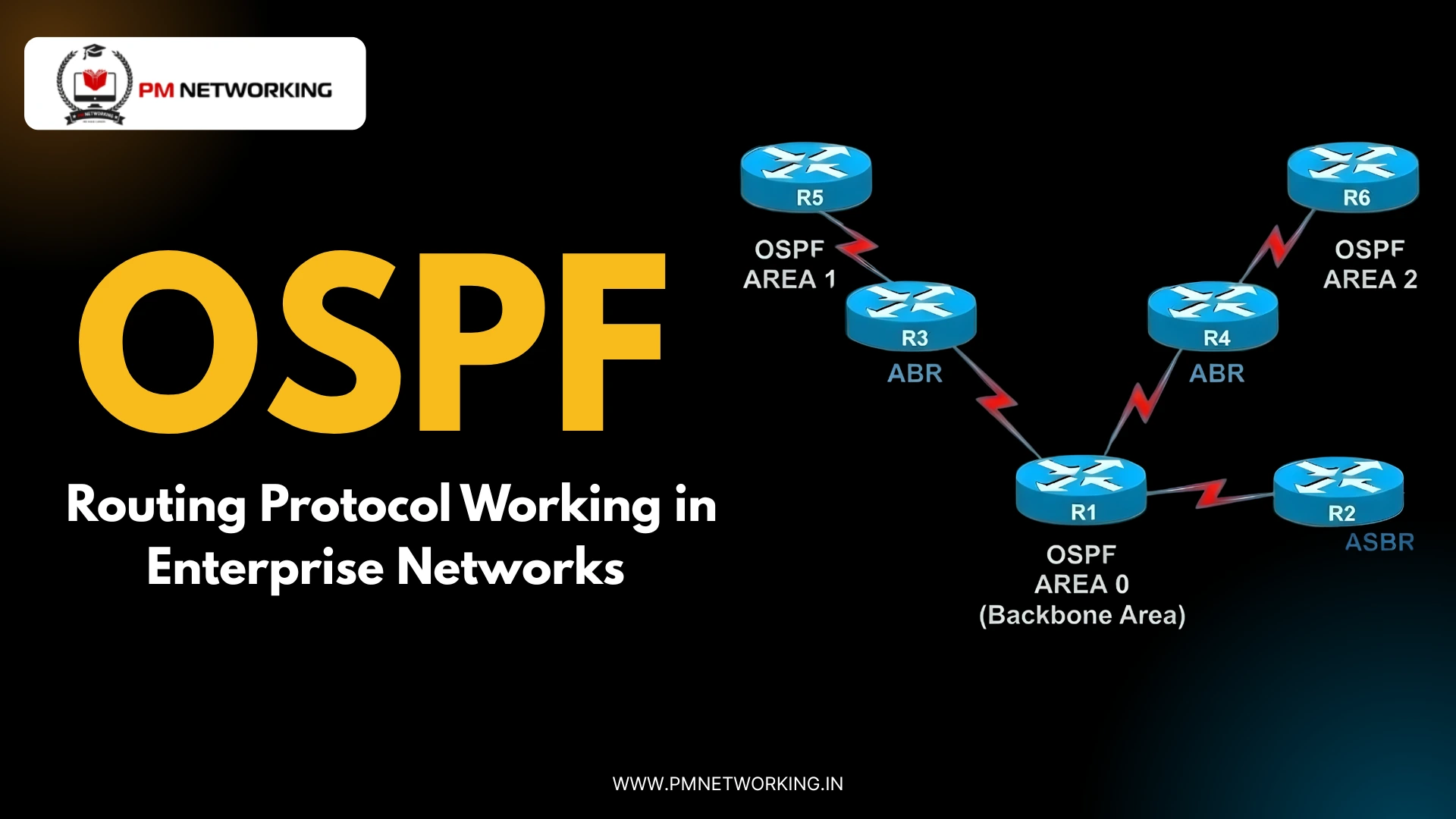
- OSPF creates a map of complete topology on the basis of “AREAS”.
- Area-id is a 32 bits address that is represented in the form of IPv4. The IPv4 representation of Area 0 is 0.0.0.0. (Area ID = 32 bit = 0 — 4.3 billion)
- Mainly there are two types of areas in OSPF. Backbone Area and Non-backbone Area (Regular, Normal) Area.
- Area 0 is called the backbone Area and all the Areas except Area 0 are called the non-backbone Area or can say Normal Area.
Two OSPF Routers can become neighbors only if Area-id will match of both Routers.
There Are Four Types Of Routers In OSPF :
- Backbone Router
- Non-Backbone Router
- ABR (Area Border Router)
- ASBR (Autonomous System Border Rouer)
Backbone Router: A Router Whose All Interfaces are Connected in Backbone Area (Area 0) is known as Backbone Router.
Area 0 should be centralized and located between all non-backbone areas.
There should not be more than one area 0 in the OSPF domain.
Non-Backbone Router: Router Whose All Interfaces Belongs To Internal Area is known as Backbone Router.
ABR (Area Border Router): A router whose at least one interface is connected to Backbone Area (Area 0) and at least one is connected to the Internal Area that type of Router is known as Area Border Router. It connected different areas together. ABR will automatically exchange routes from one area into another area without redistribution. ABRs will have the complete database of each area they are connected to ABR.
A router whose at least one interface is connected to the Area and at least one is connected to Internal Area.
ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router):
A router whose at least one interface is connected to OSPF Domain and at least one Interface connected to any other Domain that type of Router is known as ASBR.

In the above Topology, As you can see all interfaces of Router 3 are in Area 0 which means Router 3 is a Backbone Router.
Look at R1 and R6, As You can see all interfaces of Router 1 and Router 6 are in Area 10 (Non-Backbone Area) Which means Router 1 and Router 6 are Non-Backbone Routers.
Look at R2, As you can see one interface of Router 2 is in Area 0 (Backbone Area) and One interface is in Area 10 (Non-Backbone Area) which means Router 2 is ABR (Area Border Router).
Look at R4, As you can see One interface of Router 4 is in Area 0 (Backbone Area) and One interface is in Area 5 (Non-Backbone Area) which means Router 4 is also an ABR (Area Border Router).
Look at R5, As you can see One interface of Router 5 is in OSPF Domain and One interface is in EIGRP Domain (Any other Domain) which means Router 5 is ASBR (Autonomous System Border Router).
- OSPF Uses SPF Algorithm to calculate best path.
- Administrative Distance of OSPF is 110.
- By default Auto Summary is Disable in OSPF.
- OSPF is an Classless Routing Protocol.
- OSPF Supports Unlimited Hop Count.
OSPF Neighborship :
As soon as you enable OSPF on the interface of the Router, The Router will start sending a hello message from that particular interface periodically and wait to receive a hello message on that interface once OSPF Enabled interface receives a hello message they will check some parameters If those parameters will match then only they will form a neighbor relationship with each other.
What are those parameters:
- Area id must be the same in both (Sent and Received) hello messages.
- The subnet and Subnet Mask Must be the same.
- Hello, and Dead timers must be the same.
- The Router id Must be Unique within Area.
- Authentication must match If Configured. (Type 0 = Null, Type 1 = Pain Text, Type 2 = MD5)
- OSPF Network Type must match.
- OSPF Stub Flag must match.
OSPF Process-ID :
Process-ID is a 16 bits value represented in Decimal.
We can run multiple OSPF Processes on a single Router and Process-ID is used to identify the OSPF Process. You can have the same or different process IDs on different Routers.
OSPF Router never advertises Process-ID in Updates.
OSPF Router-ID :
Router id is a 32 Bits value in the form of IPv4 which is used to identify the device from which a packet originated.
It is a Unique Identification of the Router in the OSPF Domain, Router id must be unique in OSPF Area.
It Should be unique within an area of all routers.
Election Process of Router-ID :
OSPF uses the following criteria to select the Router-id
1. Manual Configuration of the Router id.
2. Highest IP address on a loopback interface.
3. Highest IP address on a physical interface.
Let’s see this practically:

There are two physical interfaces and two loopback interfaces. All interfaces are active:

Let’s enable OSPF on this Router:

Disable loopback interfaces:

It’s still the same, this is because the router ID selection is only done once. You have to reset the OSPF process before it will select another one:

Now you can see, the router ID is now the highest IP address of our physical interface.
OSPF Tables:
OSPF maintains three types of tables:
- Neighbour table
- Database table
- Routing table
By exchanging hello packets, OSPF discovers the neighbor, once the neighborship is formed, it will install neighbor information in the Neighbor table after that OSPF exchanges the link-state advertisements(LSAs), and the OSPF router installs link-state advertisements(LSAs) in their Database then OSPF runs SPF algorithm on their Database and calculates the best path which OSPF router installs in their Routing table.
Types of Messages in OSPF:
There are five types of Messages/packets in OSPF:
- Hello Message
- DBD (Database Description)
- LSR (Link State Request)
- LSU (Link State Update)
- LSAck (Link State Acknowledgment)
Hello Packet: It is used to discover the neighbor and Keep them alive. The hello packets are sent at a configurable interval (in seconds). The default is 10 seconds for an Ethernet link and 30 seconds for a non-broadcast link. The Hello packets include a list of all neighbors for which a hello packet has been received with the dead interval. The dead interval is also a configurable interval (in seconds), and the default is four times the value of the hello interval.
The value of all hello intervals must be the same within a network. Likewise, the value of all dead intervals must be the same within a network.
If a router does not receive a hello packet within the dead interval, it will declare that neighbor to be down.
Contents of a Hello Packet:
- OSPF Version
- Message Type
- Packet Length
- Router ID
- Area ID
- Packet Checksum
- Authentication Type
- Authentication Data
> Type 0 = Null
> Type 1 = Plain Text
> Type 3 = MD5 - Network Mask
- Hello Time
- Hold Down Time
- Priority
- Neighbor Router ID
- DR Router ID
- BDR Router ID
PM Networking is an emerging leader in the ed-tech space, founded by Praphul Mishra in 2020 with a vision to democratize tech education. The journey of PM Networking began as a YouTube channel with the sole purpose of sharing valuable knowledge in the fields of Networking, Cyber Security, and Cloud Computing. What started as a humble effort to educate has rapidly evolved into a comprehensive online learning platform that caters to the growing demand for specialized IT skills. PM Networking stands out in the crowded ed-tech industry by providing affordable, world-class training tailored to the needs of aspiring IT professionals. The platform is dedicated to equipping learners with the skills and knowledge required to excel in the highly competitive tech industry. Whether it’s Networking fundamentals, advanced Cyber Security protocols, or mastering the complexities of Cloud Computing, PM Networking offers a range of courses designed to cater to different levels of expertise.



0 Comments